Uric Acid
Uric acid is a heterocyclic compound that is a natural byproduct of the metabolism of purine, a nitrogen-containing compound found in many foods. The human body produces uric acid as a waste product when it breaks down purines from food and other sources. Uric acid is typically dissolved in the blood and excreted by the kidneys in urine, but when the body produces too much uric acid or is unable to eliminate it effectively, it can lead to a condition called hyperuricemia.
Hyperuricemia can result in the formation of urate crystals in the joints and tissues, causing inflammation and pain. This condition is known as gout, and it can cause debilitating attacks of pain, stiffness, and swelling. In addition to gout, high levels of uric acid have been associated with other health problems such as kidney stones, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes.
1. Definition and Chemical Structure
Uric acid is a heterocyclic compound with the chemical formula C5H4N4O3. It is a weak acid that is formed when the body breaks down purines, which are nitrogen-containing compounds found in many foods. The structure of uric acid consists of a purine ring fused with an imidazole ring.
2. Functions in the Body
Uric acid is a natural waste product that is produced when the body breaks down purines from food and other sources. In small amounts, uric acid has antioxidant properties and may help protect against oxidative damage to cells. However, high levels of uric acid can lead to health problems.
3. Sources of Uric Acid
The body produces uric acid as a waste product of purine metabolism. Purines are found in many foods, particularly organ meats such as liver, kidneys, and sweetbreads, as well as in seafood, game meats, and some vegetables such as asparagus, spinach, and mushrooms.
a. Hyperuricemia
Hyperuricemia is a condition in which there is an excess of uric acid in the blood. This can occur due to either overproduction of uric acid by the body or the inability of the kidneys to excrete it effectively. Risk factors for hyperuricemia include a diet high in purines, obesity, alcohol consumption, certain medications such as diuretics, and some medical conditions such as hypertension, metabolic syndrome, and kidney disease.
b.Symptoms and Diagnosis
Hyperuricemia itself does not typically cause symptoms. However, when uric acid levels are very high, it can lead to the formation of urate crystals in the joints and tissues, causing painful inflammation known as gout. In some cases, high levels of uric acid can also lead to the formation of kidney stones.
c. Symptoms of Uric Acid
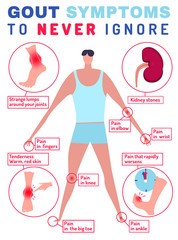
High levels of uric acid in the body can cause a condition called hyperuricemia, which can lead to a variety of symptoms. Some of the main symptoms of hyperuricemia include:
- Joint pain and swelling: High levels of uric acid can lead to a type of arthritis called gout, which causes sudden and severe joint pain, swelling, and inflammation, typically in the big toe. Gout attacks can also occur in other joints, such as the ankle, knee, wrist, and elbow.
- Kidney stones: Uric acid crystals can also form in the kidneys, leading to the formation of kidney stones. Symptoms of kidney stones may include severe pain in the back or side, nausea and vomiting, and blood in the urine.
- Fatigue: Hyperuricemia can also cause feelings of fatigue and weakness.
- Sleeping Difficulty: Some people with hyperuricemia may experience difficulty sleeping due to pain or discomfort.
- Redness and Warmth: Inflamed joints can become red, swollen, and warm to the touch.
- Limited range of motion: Joint pain and swelling can make it difficult to move the affected joint.
- It is also linked to diseases like diabetes, renal disease, and heart disease due to elevated uric acid levels.
- Gout causes excruciating joint discomfort.
- Stiff joints.
- Afflicted joints have trouble moving.
- Oedema and redness.
- Irregular joints.
It’s important to note that not everyone with high levels of uric acid will experience symptoms, and some people may have hyperuricemia without developing gout or kidney stones. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
4. Causes of Uric Acid
Fructose-rich foods and beverages should not be consumed (a type of sugar). Eating a lot of purines in your diet, which your body converts to uric acid. Red meat, organ meat meals., and some varieties of seafood, including anchovies, sardines, mussels, scallops, trout, and tuna, are purine-rich
Uric acid is produced when the body breaks down purines from food. Normally, it is dissolved in the blood and excreted through urine. However, if there is an excess of uric acid or the kidneys can’t eliminate it properly, it can lead to high levels of uric acid in the blood, known as hyperuricemia. This can cause the formation of urate crystals in joints and tissues, resulting in a painful condition called gout. Other causes of hyperuricemia include a diet high in purines, obesity, alcohol consumption, certain medications, and certain medical conditions like hypertension, metabolic syndrome, and kidney disease.
Uric acid is produced when the body breaks down purines from food. It is normally eliminated by the kidneys, but if there is too much uric acid or the kidneys can’t remove it properly, it can lead to high levels of uric acid in the blood, causing gout. Other causes of high uric acid include a purine-rich diet, obesity, alcohol, certain medications, and medical conditions like hypertension, metabolic syndrome, and kidney disease.
The main cause of uric acid is the breakdown of purines, which are nitrogen-containing compounds found in many foods. When the body metabolizes purines, it produces uric acid as a waste product. Uric acid is normally dissolved in the blood and excreted by the kidneys in urine, but if the body produces too much uric acid or if the kidneys are unable to eliminate it effectively, it can lead to hyperuricemia or high levels of uric acid in the blood.
Hyperuricemia can lead to the formation of urate crystals in the joints and tissues, causing inflammation and pain, which is a condition known as gout. Other causes of hyperuricemia include a diet high in purines, obesity, alcohol consumption, certain medications, and some medical conditions such as hypertension, metabolic syndrome, and kidney disease.
A diagnosis of hyperuricemia is usually made through a blood test.
5. Can Uric Acid Go Back to Normal?
Yes, uric acid levels can go back to normal with appropriate treatment and lifestyle modifications. Treatment for hyperuricemia typically involves a combination of dietary changes, medications, and lifestyle modifications. A low-purine diet can help reduce the production of uric acid, and medications such as allopurinol and febuxostat can help reduce the production of uric acid or increase its excretion by the kidneys. Lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise, weight management, and limiting alcohol consumption can also help manage hyperuricemia.
It’s important to note that managing hyperuricemia is a lifelong process, and it may take some time for uric acid levels to go back to normal. Additionally, some people may require ongoing treatment to maintain normal uric acid levels and prevent complications such as gout and kidney stones. It’s important to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop an appropriate treatment plan based on individual needs and medical history.
6. The Best Foods, Herbs and Spices for Uric Acid
Dietary modifications can play an important role in managing hyperuricemia and gout. Certain foods, herbs, and spices are beneficial for reducing uric acid levels and managing gout symptoms. Here are some examples:
- Low-purine foods: Foods low in purines can help reduce uric acid levels in the body. These include most fruits and vegetables, whole grains, low-fat dairy products, and lean protein sources such as poultry and fish.
- Cherries: Cherries and cherry juice have been shown to reduce uric acid levels and inflammation in the body, making them a popular choice for managing gout symptoms.
- Ginger: Ginger has anti-inflammatory properties and can help reduce pain and inflammation associated with gout.
- Turmeric: Turmeric contains curcumin, a compound with anti-inflammatory properties that may help reduce gout symptoms.
- Green tea: Green tea contains compounds called catechins that have been found to lower uric acid levels and reduce inflammation in the body.
- https://amzn.to/3TvKcFy

- Garlic: Garlic has been found to have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, making it a potential option for managing gout symptoms.
- Flaxseeds: Flaxseeds contain lignans, which have been shown to reduce uric acid levels in the body.
- https://amzn.to/3Z27t35

- Cinnamon: Cinnamon has anti-inflammatory properties and may help reduce inflammation associated with gout.
- https://amzn.to/3TIAFLu

It’s important to note that dietary modifications should be made in consultation with a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian, as individual needs and medical history can vary. Additionally, while these foods, herbs, and spices may be beneficial for managing hyperuricemia and gout, they should not be used as a substitute for medical treatment.
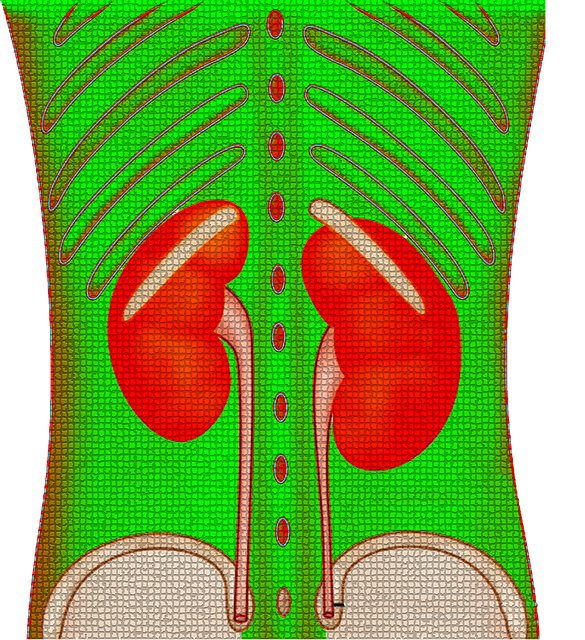
7. Most Vulnerable Body Organs in Uric Acid
The kidneys are the organs of the body that are most vulnerable to uric acid. Uric acid is a waste product that is normally excreted by the kidneys, but when there is an excess of uric acid in the body, the kidneys can become overwhelmed and are unable to remove it efficiently. This can lead to the formation of urate crystals in the kidneys, which can cause kidney stones and potentially lead to kidney damage if left untreated.
In addition, hyperuricemia can also lead to the development of gout, a painful form of arthritis caused by the accumulation of urine crystals in the joints. If gout is left untreated or poorly managed, it can lead to joint damage and deformity.
It’s important to note that while the kidneys are the most vulnerable organ in hyperuricemia, other organs and systems in the body can also be affected. High levels of uric acid have been linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, hypertension, and metabolic syndrome, which can affect multiple organ systems in the body. Therefore, it’s important to work closely with a healthcare provider to manage hyperuricemia and prevent potential complications.
8. What Happens if Uric Acid is High?
If uric acid levels in the blood are high, it can lead to a condition known as hyperuricemia. Hyperuricemia can cause a range of symptoms and potential health complications.
- Gout: The most common complication of hyperuricemia is gout, a type of arthritis that is caused by the accumulation of urine crystals in the joints. Gout typically affects the big toe, but it can also affect other joints in the body such as the ankle, knee, and elbow. Symptoms of gout include sudden, severe pain, swelling, redness, and stiffness in the affected joint.
- Kidney stones: High levels of uric acid in the blood can also lead to the formation of kidney stones, which are small, hard deposits that can cause pain and discomfort when passing through the urinary tract.
- Kidney disease: Hyperuricemia can also increase the risk of kidney disease and damage. High levels of uric acid can lead to the formation of urate crystals in the kidneys, which can cause inflammation and damage to the kidneys over time.
- Hypertension: Studies have found that hyperuricemia is associated with an increased risk of hypertension, or high blood pressure.
- Metabolic syndrome: Hyperuricemia has also been linked to an increased risk of metabolic syndrome, a cluster of conditions that include high blood pressure, high blood sugar, abnormal cholesterol levels, and excess abdominal fat.
- Cardiovascular disease: High levels of uric acid in the blood have been associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, including heart attack and stroke.
It’s important to note that not everyone with hyperuricemia will experience symptoms or complications. However, it’s important to manage high uric acid levels to prevent potential complications and maintain overall health. Treatment typically involves a combination of dietary modifications, lifestyle changes, and medication. It’s important to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop an appropriate treatment plan based on individual needs and medical history.
9. Fruits and Vegetables Useful in Uric Acid
Several fruits and vegetables are useful in managing uric acid levels. Here are some examples:
- Cherries: Cherries and cherry juice are effective in reducing uric acid levels and preventing gout attacks. This is believed to be due to their anti-inflammatory properties.
- Berries: Berries such as strawberries, blueberries, and raspberries are rich in vitamin C and antioxidants, which can help lower uric acid levels and reduce inflammation.
- Pineapple: Pineapple contains an enzyme called bromelain, which has anti-inflammatory properties and can help reduce inflammation and pain associated with gout.
- Apples: Apples are high in malic acid, which has been found to help dissolve uric acid in the body and promote its elimination.
- Citrus fruits: Citrus fruits such as oranges, grapefruits, and tangerines are high in vitamin C, which can help lower uric acid levels and reduce inflammation.
- Leafy greens: Leafy greens such as spinach, kale, and broccoli are high in vitamin C and other antioxidants, which can help lower uric acid levels and reduce inflammation.
- Tomatoes: Tomatoes are high in vitamin C and lycopene, which have been found to lower uric acid levels and reduce inflammation.
It’s important to note that while these fruits and vegetables can help manage uric acid levels, they should not be used as a substitute for medical treatment. It’s important to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop an appropriate treatment plan based on individual needs and medical history.
10. Lemon Grass and Moringa Tea
Lemongrass and moringa tea are two types of herbal teas that have been traditionally used in various cultures for their medicinal properties. While there is some limited research suggesting that they may have potential benefits for uric acid levels, more studies are needed to fully understand their effects.


Lemongrass tea is a popular herbal tea made from the leaves of the lemongrass plant. Some research suggests that lemongrass may have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, which could help reduce inflammation and oxidative stress associated with hyperuricemia. However, there is limited research specifically examining the effects of lemongrass tea on uric acid levels in humans.
Moringa tea is made from the leaves of the moringa tree and is rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Some studies suggest that moringa may have anti-inflammatory and hypouricemic effects, which means that it may help lower uric acid levels in the blood. However, more research is needed to fully understand its effects and determine the appropriate dosage and duration of use.
It’s important to note that while herbal teas like lemongrass and moringa may have potential health benefits, they should not be used as a substitute for medical treatment. It’s important to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop an appropriate treatment plan based on individual needs and medical history. In addition, some herbal teas can interact with medications or have potential side effects, so it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new herbal tea or supplement.
11. The Simple Preventive /Remedial Measures to Safeguard from Uric Acid
Several simple preventive and remedial measures can help safeguard against high levels of uric acid and gout. Here are some examples:
- Maintain a healthy weight: Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of developing high levels of uric acid and gout. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can help reduce this risk.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water and other fluids can help flush out uric acid from the body and prevent its buildup.
- Limit alcohol consumption: Alcohol can increase uric acid production and reduce the body’s ability to eliminate it, so it’s important to limit or avoid alcohol consumption, particularly beer and spirits.
- Choose low-purine foods: Purines are substances found in certain foods that can increase uric acid levels in the body. Choosing low-purine foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein sources can help reduce the risk of hyperuricemia and gout.
- Avoid high-purine foods: Some foods are particularly high in purines and should be avoided or limited in the diet, including red meat, organic meats, seafood, and some types of beans and lentils.
- Consider supplements: Some supplements such as vitamin C https://amzn.to/3luwnL3

- , cherry extract and omega-3 fatty acids may help reduce inflammation and lower uric acid levels. However, it’s important to talk to a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement.
- https://amzn.to/3n7oawR

Fish Oil - https://amzn.to/3JXFhu5

- Manage stress: Stress can trigger gout attacks, so it’s important to manage stress through relaxation techniques, such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing.
- Take Prescribed Medications: For some people with hyperuricemia or gout, medications may be necessary to control uric acid levels and prevent gout attacks. It’s important to take any prescribed medications as directed by a healthcare provider.
By following these simple preventive and remedial measures, it’s possible to reduce the risk of hyperuricemia and gout and promote overall health and well-being. It’s important to work closely with a Doctor to develop an appropriate treatment plan based on individual needs and medical history.
Disclaimer: The contents of this article are intended to raise awareness about common health issues and should not be viewed as sound medical advice for your specific condition. You should always consult with a licensed medical practitioner before following any suggestions outlined in this article or adopting any treatment protocol based on the contents of this article.
If you enjoyed this article, please like and share it with your friends, and don’t forget to subscribe for more great content!