Gut health, Gut-brain connection, Digestive wellness, Gut microbiota, Gut-brain axis, Mental health, Emotional well-being, Unhealthy gut, Balanced gut microbiome, Probiotics and prebiotics, Fibre-rich foods, Fermented foods, Chronic inflammation, Stress management, Exercise and digestion, Food intolerances, Weight management, Gut lining repair, Healthy lifestyle habits, Gut health signals
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on understanding gut health and its impact on overall well-being. In this article, we will explore the fascinating world of the digestive system, explore the gut-brain connection, discuss the factors affecting gut health, and provide strategies for improving digestive wellness. Let’s begin!
1. Introduction to Gut Health
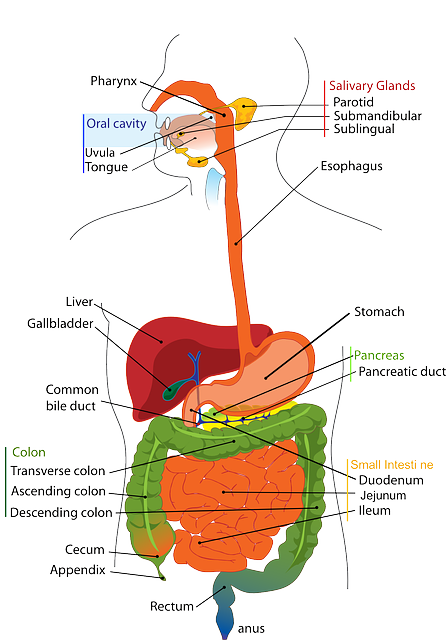
The digestive system plays a crucial role in our overall health. It is responsible for breaking down food, absorbing nutrients, and eliminating waste products. Not only does the digestive system support our physical well-being, but it also influences our mental and emotional health. 
A key player in gut health is the gut microbiota, which refers to the trillions of microorganisms living in our digestive tract. These microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi, form a complex ecosystem that has a profound impact on our well-being.
2. The Gut-Brain Connection
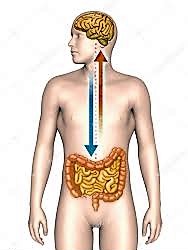 The gut-brain connection, also known as the gut-brain axis, describes the bidirectional communication between the gut and the brain. This intricate network allows the two organs to influence each other and significantly impacts our health. At the core of this connection is the vagus nerve, a long cranial nerve that runs from the brainstem to the abdomen. The vagus nerve plays a vital role in transmitting signals between the gut and brain, influencing various physiological processes.
The gut-brain connection, also known as the gut-brain axis, describes the bidirectional communication between the gut and the brain. This intricate network allows the two organs to influence each other and significantly impacts our health. At the core of this connection is the vagus nerve, a long cranial nerve that runs from the brainstem to the abdomen. The vagus nerve plays a vital role in transmitting signals between the gut and brain, influencing various physiological processes.
The gut-brain connection is bidirectional, meaning that the state of our gut health can influence our mental and emotional well-being, while our brain’s state can affect our digestive function.
3. Impact of Gut Health on Overall Well-being
Our gut health has a profound impact on our overall well-being. Research has shown that an unhealthy gut can contribute to various mental health issues, such as depression, anxiety, and mood disorders.
Furthermore, emerging studies have linked gut health to neurological conditions like Alzheimer’s disease. The gut microbiota’s composition and diversity play a crucial role in brain health and the development of neurodegenerative diseases.
Gut health also influences our immune system and overall inflammation levels. A healthy gut supports a robust immune response, while imbalances in the gut microbiota can lead to immune dysregulation and chronic inflammation.

4. Factors Affecting Gut Health
• Diet and Nutrition:
A balanced diet rich in fiber, fruits, vegetables, and fermented foods promotes healthy gut microbiota. Fibre acts as a prebiotic, providing nourishment for beneficial gut bacteria. On the other hand, processed foods, excessive sugar, and artificial additives can disrupt the delicate balance of the gut microbiota, leading to digestive issues.
• Stress and Lifestyle Factors:
Chronic stress can negatively impact gut health by altering gut microbiota composition and impairing digestive function. Engaging in stress management techniques, regular exercise, and ensuring sufficient sleep are crucial for maintaining a healthy gut.
• Medications and Antibiotics:
Certain medications, such as antibiotics, can disrupt the gut microbiota by eliminating both harmful and beneficial bacteria. It is essential to consult healthcare professionals and use medications judiciously to minimize their impact on gut health.
5. Strategies for Improving Digestive Wellness
Probiotics and Prebiotics:
The role of probiotics in promoting healthy gut microbiota is crucial for maintaining digestive wellness. Probiotics are live microorganisms that, when consumed in adequate amounts, provide a beneficial effect on the host’s health. These friendly bacteria help balance the composition of the gut microbiota, which is a community of microorganisms residing in our digestive system.

Probiotics work by supporting the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut, inhibiting the growth of harmful bacteria, and strengthening the gut barrier. They aid in digestion, nutrient absorption, and the production of certain vitamins. Moreover, probiotics have been associated with improved immune function and reduced inflammation.
There are various food sources rich in probiotics that can be incorporated into the diet. Fermented foods are particularly abundant in beneficial bacteria. Examples include:
a. Yoghurt: Look for yogurts labeled with “live and active cultures” as they contain specific strains of probiotics like Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium.
b. Kefir: A fermented milk drink that contains a diverse range of probiotic strains.
c. Sauerkraut: Fermented cabbage that provides probiotics along with fiber and nutrients.
d. Kimchi: A traditional Korean dish made from fermented vegetables, often including cabbage, radishes, and spices.
e. Kombucha: A fermented tea beverage that contains probiotics and is known for its fizzy nature.
In addition to food sources, probiotic supplements are also available. These supplements provide concentrated doses of specific probiotic strains. It’s important to choose high-quality supplements from reputable brands and consult with a healthcare professional for personalized recommendations.
Prebiotics, on the other hand, are non-digestible fibers that act as food for probiotics, promoting their growth and activity in the gut. They help create a favorable environment for the probiotics to thrive. Some common food sources rich in prebiotics include:

a. Chicory root: A natural source of inulin, a prebiotic fibre. https://amzn.to/3N5ZP3C

b.Garlic: Contains inulin and other prebiotic compounds.
c. Onions: Provide a good amount of inulin and other prebiotic fibers.Bananas: Rich in a prebiotic fiber called resistant starch.
d. Jerusalem artichoke: Contains inulin and other prebiotic fibers. https://amzn.to/43KjoG5

Incorporating a variety of probiotic-rich foods and prebiotic sources into your diet can contribute to healthy gut microbiota. However, it’s essential to remember that individual responses to probiotics and prebiotics may vary, and consulting with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian is recommended for personalized guidance and advice.
6. Dietary Recommendations:
Improving gut health through dietary choices is an effective way to support digestive wellness. Here are some dietary tips to enhance gut health:
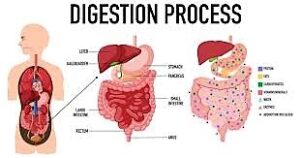
- Consume Fermented Foods: Incorporating fermented foods into your diet provides a natural source of probiotics. Foods such as yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, and kombucha contain live bacteria that can help populate your gut with beneficial microorganisms, improving the balance of the gut microbiota.
- Drink Enough Water: Staying adequately hydrated is vital for proper digestion and maintaining optimal gut health. Water helps soften the stool, prevents constipation, and supports the smooth movement of food through the digestive system. Aim to drink at least 8 glasses of water per day, or more if needed.
- Limit Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol intake can disrupt the gut microbiota and damage the lining of the intestines. It’s advisable to consume alcohol in moderation or avoid it altogether to maintain a healthy gut. If you choose to drink, do so in moderation and consider opting for lower-alcohol options.
- Moderate Caffeine Intake: While moderate caffeine consumption is generally well-tolerated, excessive intake can stimulate the gut and lead to digestive discomfort. Be mindful of your caffeine intake from sources such as coffee, tea, energy drinks, and chocolate. Consider switching to herbal teas or reducing your caffeine intake if you experience gut-related symptoms.
- Minimize Processed and Sugary Foods: Highly processed foods and those high in added sugars can negatively impact gut health. These foods often lack fiber and beneficial nutrients, while promoting the growth of harmful bacteria. Opt for whole, unprocessed foods and limit your intake of sugary treats and processed snacks.
- Practice Mindful Eating: Slow down and be mindful of your eating habits. Chew your food thoroughly, and take time to enjoy and savor each bite. Mindful eating helps promote proper digestion and allows you to tune in to your body’s hunger and fullness cues.
- Consider Food Intolerances: If you suspect certain foods are causing digestive discomfort, consider keeping a food diary to identify potential triggers. Common culprits include gluten, lactose, and specific FODMAPs (fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides, and polyols). Consult a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for guidance on elimination diets or appropriate dietary modifications.
Remember that individual dietary needs may vary, and it’s important to listen to your body and make adjustments that work best for you. Incorporating these dietary tips along with a balanced and varied diet can help improve gut health and support overall well-being.
7. Lifestyle Modifications:
Making certain lifestyle modifications can significantly contribute to improving gut health. Here are some key areas to focus on:
- Stress Reduction Techniques: Chronic stress can negatively impact gut health by disrupting the balance of the gut microbiota and affecting digestive processes. Engaging in stress reduction techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and mindfulness practices, and engaging in hobbies or activities you enjoy can help lower stress levels and promote a healthier gut.
- Regular Exercise: Regular physical activity has been linked to improved gut health. Exercise helps stimulate the muscles of the digestive system, promoting more efficient digestion and reducing the risk of constipation. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming.
- Quality Sleep: Getting sufficient and restful sleep is crucial for overall health, including gut health. Lack of sleep can disrupt the gut microbiota and increase the risk of gastrointestinal issues. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night by establishing a consistent sleep routine, creating a comfortable sleep environment, and practicing relaxation techniques before bed.
- Relaxation Methods: Incorporating relaxation methods like meditation, yoga, or tai chi into your routine can have a positive impact on gut health. These practices help activate the body’s relaxation response, reducing stress levels and promoting better digestion. Find a relaxation method that resonates with you and allocate time each day for its practice.
- Hydration: Staying well-hydrated is essential for optimal gut function. Drinking an adequate amount of water helps maintain regular bowel movements and supports the overall health of the digestive system. Aim to drink water throughout the day and pay attention to your body’s hydration needs, especially during physical activity or in hot weather.
Remember, everyone’s lifestyle needs are unique, so it’s essential to find a balance that works for you. Incorporating stress reduction techniques, regular exercise, quality sleep, and relaxation methods into your daily routine can positively impact gut health and contribute to overall well-being. Listen to your body’s signals make adjustments accordingly, and consult with healthcare professionals or wellness experts for personalized advice.
8. Avoiding Gut Irritants:
Avoiding gut irritants is crucial for maintaining a healthy gut and minimizing digestive discomfort. Here are some common gut irritants to be aware of:
- Certain Foods: Some foods can irritate the gut and trigger digestive symptoms in susceptible individuals. These may include spicy foods, greasy or fried foods, processed foods high in artificial additives, and foods high in lactose or gluten for those with intolerances or sensitivities. It’s important to pay attention to how your body reacts to different foods and identify any specific triggers that may cause digestive issues.
- Alcohol: Excessive alcohol consumption can irritate the lining of the digestive system, leading to inflammation and digestive discomfort. Alcohol can also disrupt the balance of the gut microbiota, contributing to gut dysbiosis. Limiting alcohol intake or avoiding it altogether can help reduce gut irritation and promote a healthier digestive system.
- Smoking: Smoking is known to have numerous detrimental effects on overall health, including the digestive system. Smoking can increase the risk of developing gastrointestinal disorders such as peptic ulcers, acid reflux, and Crohn’s disease. Quitting smoking or avoiding exposure to secondhand smoke is essential for maintaining a healthy gut.
Identifying and avoiding personal triggers is crucial for managing gut irritants effectively. Here’s why it’s important:
- Individual Sensitivities: Each person’s digestive system is unique, and what irritates one person’s gut may not affect another in the same way. By identifying personal triggers, you can tailor your diet and lifestyle choices to suit your specific needs, minimizing gut irritation and optimizing digestive wellness.
- Symptom Management: Knowing your triggers allows you to proactively manage and reduce the occurrence of digestive symptoms. By avoiding foods or substances that irritate your gut, you can alleviate symptoms such as bloating, gas, abdominal pain, diarrhea, or constipation.
- Gut Healing: Avoiding irritants gives your gut a chance to heal and restore its natural balance. This is especially important if you have experienced gut-related conditions or disorders, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
To identify your triggers, consider keeping a food diary to track your diet and symptoms. Note any correlations between specific foods, alcohol consumption, smoking, or other factors and your digestive symptoms. If you suspect certain foods are causing issues, you may want to consider an elimination diet under the guidance of a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian to pinpoint problem foods.
By avoiding gut irritants based on personal triggers, you can reduce digestive discomfort, promote gut healing, and support a healthier and happier gut.
9 . Seeking Professional Advice
Seeking professional advice is of utmost importance when it comes to addressing specific gut health concerns. Consulting healthcare professionals, such as doctors or registered dietitians, can provide personalized guidance and support tailored to your individual needs. Here’s why it’s crucial to seek professional advice:
- Accurate Diagnosis: Healthcare professionals have the expertise to accurately diagnose and assess gut health issues. They can evaluate your symptoms, and medical history, and conduct necessary tests to determine the underlying causes of your gut-related concerns. This enables targeted and effective treatment strategies.
- Personalized Approach: Every individual is unique, and gut health is a complex matter. Professionals can take into account your specific circumstances, medical conditions, dietary habits, and lifestyle factors to develop a personalized plan to improve your gut health. This approach ensures that the recommendations are tailored to your specific needs, promoting optimal results.
- Expert Guidance: Healthcare professionals, particularly registered dietitians, are well-versed in the complexities of nutrition and gut health. They can provide evidence-based advice on dietary modifications, recommend suitable probiotics or supplements if necessary, and guide you through the process of implementing positive changes to support your gut health journey.
- Monitoring Progress: Regular follow-up with healthcare professionals allows for the monitoring of your progress and the adjustment of treatment plans as needed. They can help you navigate any challenges or setbacks you may encounter and provide ongoing support to ensure you stay on track toward improved gut health.
- Managing Underlying Conditions: Gut health issues can be linked to underlying medical conditions, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), or food intolerances. Healthcare professionals can diagnose and manage these conditions, helping you navigate the complexities of gut health in the context of any coexisting health conditions.
Remember, the information provided in this article is general in nature and may not address your specific circumstances. If you have persistent or severe gut health concerns, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional for a comprehensive evaluation and individualized advice. They can provide you with the appropriate tools and strategies to optimize your gut health and overall well-being.
- The digestive system and its significance in maintaining good health.
- The role of the gut macrobiotic in gut health and its complex ecosystem.
- The gut-brain connection and how the gut and brain communicate through the vagus nerve.
- The bidirectional relationship between gut health and mental well-being, including mood, anxiety, and stress levels.
- The link between gut health and neurological conditions like depression and Alzheimer’s disease.
- The influence of gut health on immune function and overall inflammation levels.
- Factors affecting gut health, such as diet and nutrition, stress and lifestyle factors, and certain medications and antibiotics.
- Strategies for improving digestive wellness, include the use of probiotics and prebiotics, dietary recommendations, lifestyle modifications, and avoiding gut irritants.
- The importance of seeking professional advice from healthcare professionals for personalized guidance.
- The overall significance of understanding and improving gut health for enhancing overall well-being.
7. Conclusion: It is crucial to prioritize gut health as it not only supports digestion but also impacts mental health, immune function, and inflammation levels. By adopting a balanced diet, managing stress, and making lifestyle adjustments, individuals can optimize their gut health and experience improved overall well-being.
If you enjoyed this article, please like and share it with your friends, and don’t forget to subscribe for more great content!
DISCLAIMER: The contents of this article are intended to raise awareness about common health issues and should not be viewed as sound medical advice for your specific condition. You should always consult with a licensed medical practitioner before following any suggestions outlined in this article or adopting any treatment protocol based on the contents of this article.