Understanding Pakistan’s Water Scarcity Issues: Confronting the Looming Threat in 2025
Discover the root causes and far-reaching consequences of Pakistan’s water scarcity issues. Learn how this crisis affects the country’s food security, economy, and inhabitants.
Pakistan, a country with an abundance of natural resources, is facing a severe water crisis. The nation’s water scarcity issues have become a pressing concern, affecting millions of lives, the economy, and the environment. In this article, we will delve into the root causes, consequences, and potential solutions to this looming threat.

The scope of the crisis can be demonstrated by a few key facts:
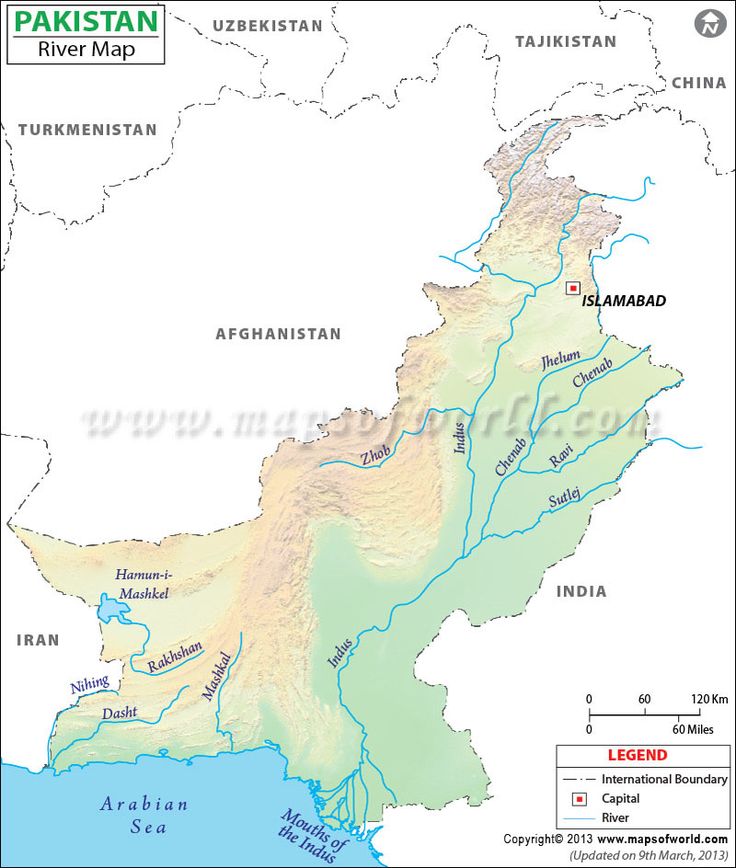
- About 92 per cent of Pakistan is classified as semi-arid to arid, and the vast majority of Pakistanis are dependent on surface and groundwater sources from a single source—the Indus River basin.
- Since gaining independence in 1947, Pakistan’s population has more than quadrupled; by 2100 its population will have increased by tenfold.
- About 90 per cent of the country’s agricultural production comes from land irrigated by the Indus Basin Irrigation System (Qureshi, 2011), firmly linking national food security to water levels in the Indus River basin.
- Pakistan’s water storage capacity is limited to a maximum 30-day supply, far below the 1,000-day storage capacity recommended for a country with its climatic characteristics.
The Alarming Reality: Water Scarcity in Pakistan
Pakistan is among the top 10 countries facing severe water scarcity. The country’s per capita water availability has dwindled significantly, from 5,260 cubic meters in 1951 to a mere 1,000 cubic meters today. This drastic reduction has resulted in a severe water crisis, impacting various sectors, including agriculture, industry, and domestic consumption.
Pakistan’s Water Management System: Challenges and Opportunities
Pakistan’s water management system is a complex network of institutions, infrastructure, and policies that govern the country’s water resources. The system faces numerous challenges, including inefficient water use, inadequate infrastructure, and climate change. This article will explore the current state of Pakistan’s water management system, its challenges, and potential opportunities for improvement.
Current State of Water Management in Pakistan
Pakistan’s water management system is overseen by the Ministry of Water Resources, which is responsible for policy-making, planning, and coordination. The system comprises:
-
Water Infrastructure: Pakistan has an extensive network of dams, barrages, canals, and watercourses that store, divert, and distribute water for irrigation, drinking, and industrial purposes.
-
Irrigation Department: The irrigation department is responsible for managing the water infrastructure, maintaining canals, and distributing water to farmers.
-
Water and Power Development Authority (WAPDA): WAPDA is responsible for developing and maintaining the country’s water and power resources, including dams, hydropower plants, and irrigation systems.
Challenges Facing Pakistan’s Water Management System
Despite its complexities, Pakistan’s water management system faces numerous challenges, including:
-
Inefficient Water Use: Pakistan’s agriculture sector, which accounts for over 90% of the country’s water use, is characterized by inefficient irrigation practices, resulting in significant water losses.
-
Ageing Infrastructure: Pakistan’s water infrastructure is ageing and in need of repair and maintenance. This has resulted in significant water losses and reduced the system’s overall efficiency.
-
Climate Change: Climate change is altering precipitation patterns, leading to more frequent and severe droughts and floods. This poses significant challenges to Pakistan’s water management system.
-
Institutional Weaknesses: Pakistan’s water management institutions are often weak and fragmented, leading to coordination challenges and inefficient decision-making.
Opportunities for Improvement
Despite the challenges, there are opportunities for improving Pakistan’s water management system, including:
-
Water Conservation: Implementing water-saving measures, such as drip irrigation and crop rotation, can reduce water waste and improve efficiency.
-
Infrastructure Upgrades: Upgrading Pakistan’s water infrastructure, including dams, canals, and watercourses, can improve the system’s efficiency and reduce water losses.
-
Institutional Reforms: Strengthening Pakistan’s water management institutions, including the Ministry of Water Resources and WAPDA, can improve coordination and decision-making.
-
Climate-Resilient Water Management: Developing climate-resilient water management practices, including water harvesting and flood management, can help Pakistan adapt to the impacts of climate change.
Pakistan’s water management system faces numerous challenges, including inefficient water use, ageing infrastructure, and climate change. However, there are opportunities for improvement, including water conservation, infrastructure upgrades, institutional reforms, and climate-resilient water management practices. By addressing these challenges and opportunities, Pakistan can improve its water management system, ensuring its citizens a more secure and prosperous future.
What do you think about Pakistan’s water management system? Share your suggestions for improvement in the comments below!
Understanding the Causes of Pakistan’s Water Scarcity Issues
Water scarcity is a growing concern worldwide, affecting millions of people and posing significant threats to the environment, economy, and human health. To address this issue, it’s essential to understand the underlying causes of water scarcity. This article will explore the main causes of water scarcity, including natural, human-induced, and climate-related factors.
Natural Causes of Water Scarcity
-
Low Rainfall: Areas with low rainfall or irregular precipitation patterns often experience water scarcity.
-
Geology: Regions with hard rock formations or limited aquifers may have restricted access to groundwater.
-
Topography: Mountainous or hilly areas can make it difficult to collect and distribute water.
Human-Induced Causes of Water Scarcity
-
Over-Extraction of Groundwater: Excessive pumping of groundwater for agriculture, industry, and domestic use can lead to depletion of aquifers.
-
Inefficient Water Use: Wasteful water practices, such as inefficient irrigation systems and leaking pipes, contribute to water scarcity.
-
Population Growth: The increasing population demands more water for drinking, sanitation, and hygiene, straining existing water resources.
-
Agricultural Practices: Water-intensive crops and farming practices can exacerbate water scarcity in agricultural areas.
-
Urbanization: Rapid urbanization can lead to increased water demand, putting pressure on existing water infrastructure.
Climate-Related Causes of Water Scarcity
-
Climate Change: Changes in precipitation patterns, increased evaporation due to rising temperatures, and altered water cycles contribute to water scarcity.
-
Droughts: Prolonged droughts can significantly reduce water availability, impacting agriculture, industry, and human consumption.
-
Extreme Weather Events: Floods and heatwaves can contaminate water sources, damage infrastructure, and disrupt water supply chains.
Addressing Water Scarcity
Understanding the causes of water scarcity is crucial for developing effective solutions. By addressing these factors through sustainable water management practices, conservation efforts, and innovative technologies, we can work towards ensuring a water-secure future for all.
What are your thoughts on the causes of water scarcity? Share your ideas for addressing this issue in the comments below!
Causes of Water Scarcity in Pakistan
Several factors contribute to Pakistan’s water scarcity issues:
-
Climate Change: Rising temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, and increased frequency of extreme weather events have significantly impacted the country’s water resources.
-
Population Growth: Pakistan’s rapidly growing population has led to increased water demand, putting a strain on the country’s limited water resources.
-
Inefficient Water Management: The lack of effective water management systems, including inadequate storage facilities and inefficient irrigation systems, exacerbates the water scarcity issue.
Consequences of Water Scarcity in Pakistan
The far-reaching consequences of Pakistan’s water scarcity issues are multifaceted:
-
Food Security: Water scarcity affects agricultural productivity, leading to reduced crop yields, decreased food security, and increased reliance on imports.
-
Economic Impact: The water crisis has significant economic implications, including reduced industrial productivity, increased costs for water treatment, and negative impacts on tourism and other sectors.
-
Health and Hygiene: Inadequate access to clean water and sanitation facilities leads to the spread of water-borne diseases, compromising public health and hygiene.
-
Environmental Degradation: Water scarcity contributes to environmental degradation, including the depletion of groundwater resources, soil salinization, and loss of biodiversity.
Pakistan Water Crisis Solutions: A Comprehensive Approach
Pakistan’s water crisis is a pressing issue that requires immediate attention and collective action. The country’s water scarcity problems are multifaceted, and solving them demands a comprehensive approach that incorporates short-term and long-term strategies. This article will outline detailed solutions to address Pakistan’s water crisis, focusing on water conservation, efficient use, and sustainable management practices.
Short-Term Solutions (2025-2030)
Water Conservation Measures:
-
Implement water-saving technologies, such as drip irrigation and sprinkler systems, in agricultural sectors.
-
Promote water-efficient appliances and fixtures in domestic and industrial settings.
-
Encourage rainwater harvesting and greywater reuse.
Repair and Maintenance of Existing Infrastructure:
-
Rehabilitate and upgrade existing dams, canals, and watercourses to reduce water losses and improve efficiency.
-
Repair and replace leaking pipes and faulty water meters.
Water Pricing and Tariff Reforms:
-
Implement a tiered water pricing system to encourage water conservation and penalize wastage.
-
Review and revise water tariffs to reflect the true value of water and generate revenue for infrastructure upgrades.
Public Awareness and Education Campaigns:
-
Launch nationwide awareness campaigns to educate citizens about the importance of water conservation and the consequences of water scarcity.
-
Integrate water education into school curricula and vocational training programs.
Medium-Term Solutions (2030-2040)
Investment in New Water Infrastructure:
-
Construct new dams, reservoirs, and water storage facilities to enhance water storage capacity and reduce dependence on rainfall.
-
Develop new canal systems and watercourses to improve irrigation efficiency and reduce water losses.
Water Recycling and Reuse:
-
Establish water recycling plants to treat wastewater for non-potable purposes, such as irrigation and industrial processes.
-
Promote the use of treated wastewater in agriculture, industry, and urban areas.
-
Agricultural Reforms:
-
Introduce water-efficient crops and farming practices, such as precision irrigation and crop rotation.
-
Encourage farmers to adopt conservation agriculture techniques, such as reduced tillage and mulching.
Institutional Reforms and Capacity Building:
-
Strengthen institutional frameworks and capacities to manage water resources effectively.
-
Establish a national water authority to oversee water policy, planning, and management.
Long-Term Solutions (2040-2050)
Climate-Resilient Water Management:
-
Develop and implement climate-resilient water management strategies to address the impacts of climate change on water resources.
-
Invest in climate-resilient infrastructure, such as flood-resistant construction and drought-tolerant crops.
Water-Energy Nexus:
-
Develop strategies to address the interlinkages between water and energy, including the water requirements for energy production and the energy requirements for water treatment and distribution.
-
Promote the use of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, to reduce the energy footprint of water management.
Innovative Technologies and Research:
-
Invest in research and development of innovative technologies, such as desalination, water recycling, and precision irrigation.
-
Promote the adoption of innovative technologies and practices in water management, agriculture, and industry.
International Cooperation and Transboundary Water Management:
-
Strengthen international cooperation and collaboration on transboundary water management issues.
-
Develop and implement agreements and frameworks for the shared management of transboundary water resources.
Implementation and Financing
The implementation of these solutions will require significant investments in infrastructure, technology, and human resources. The government, private sector, and international donors must work together to mobilize financial resources and expertise.
Conclusion
Pakistan’s water crisis demands a comprehensive and multifaceted approach. By implementing these short-term, medium-term, and long-term solutions, Pakistan can address its water scarcity challenges, ensure water security, and achieve sustainable development.
What are your thoughts on these solutions? Share your ideas and suggestions for addressing Pakistan’s water crisis in the comments below!
A Call to Action
Pakistan’s water scarcity issues demand immediate attention and collective action. It is essential for policymakers, stakeholders, and individuals to work together to address this crisis. By adopting a proactive and sustainable approach to water management, Pakistan can mitigate the impacts of water scarcity and ensure a more secure and prosperous future for its citizens.
What can you do to help? Share your thoughts and ideas on how to address Pakistan’s water scarcity issues in the comments below!

