Respiratory Problems/Cough
Respiratory problems refer to issues or disorders that affect the body’s ability to breathe properly. Some common respiratory problems include:

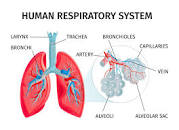
- Asthma: A chronic condition that causes inflammation and narrowing of the airways, making it difficult to breathe.
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): A group of lung diseases that make it difficult to breathe, including emphysema and chronic bronchitis.
- Pneumonia: An infection of the lungs that causes inflammation and fluid buildup in the air sacs.
- Tuberculosis (TB): A bacterial infection that primarily affects the lungs, but can also affect other parts of the body.
- Lung Cancer: A type of cancer that starts in the lung, the most common symptoms are coughing, shortness of breath, chest pain and weight loss
- Sleep Apnea: A disorder in which a person’s breathing is repeatedly interrupted during sleep.
- Bronchitis: Inflammation of the bronchial tubes, which can make breathing difficult and cause a persistent cough.
- Allergies: Allergic reactions can cause respiratory problems, including sneezing, runny nose, and difficulty breathing.
These are just some examples, and there are many other types of respiratory problems that people may suffer from. It is important to consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment.
The Diagnoses Tests/ Procedures for Different Problems
The diagnosis procedures for different respiratory problems will vary depending on the specific condition. Some common diagnostic procedures include:
- Spirometry: A test that measures the amount of air a person can inhale and exhale, and how quickly they can do it. This test can help diagnose conditions such as asthma and COPD.
- Chest X-ray: A diagnostic test that uses radiation to produce detailed images of the inside of the chest. This test can help identify problems such as pneumonia, lung cancer, and tuberculosis.
- CT scan: A diagnostic imaging test that uses X-rays and computer technology to produce detailed images of the inside of the body. This test can help identify problems such as lung cancer and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
- Bronchoscopy: A procedure that uses a thin, flexible tube with a light and camera on the end to look inside the airways. This test can help diagnose lung cancer, bronchitis, and other lung problems.
- Lung Biopsy: A procedure in which a small sample of lung tissue is removed for examination under a microscope. This test can help diagnose lung cancer and other lung problems.
- Sleep study: A procedure to monitor a person’s sleep patterns and breathing to diagnose sleep apnea and other sleep disorders
- Allergy test: A test that involves exposing the person to a small amount of an allergen and measuring the body’s reaction to it, this can help diagnose allergies
It’s worth noting that, depending on the symptoms and medical history, the doctor may require more than one test to make a diagnosis. Also, some of these tests may be used to monitor the progress of treatment and to check for complications.
Old Age is Not The Only Cause of the Problem
Old age can be a risk factor for certain respiratory problems, as the body’s ability to repair and heal itself can decline with age. For example, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and lung cancer are more common in older adults. Additionally, the risk of developing pneumonia and other lung infections increases with age.
Lung function and muscle strength also decline with age, making it harder to breathe and cough effectively, which can lead to respiratory problems such as bronchitis and pneumonia.
However, it is important to note that old age is not the only cause of respiratory problems, and many other factors such as genetics, exposure to environmental toxins, and lifestyle choices can also contribute to the development of these conditions.
So, respiratory problems can occur at any age, but older people may be more susceptible due to a decline in lung function and immune system as well as other age-related changes.
Treatment for the Patients
The treatment for respiratory problems will vary depending on the specific condition and the individual patient. Some common treatments include:
- Medications: There are a variety of medications that can be used to treat respiratory problems, including bronchodilators to open up the airways, corticosteroids to reduce inflammation, and antibiotics to treat infections.
- https://amzn.to/3AEpWcc

- Oxygen therapy: For patients with low levels of oxygen in their blood, oxygen therapy can help improve the oxygen supply to the body’s organs and tissues.
- https://amzn.to/44aReVg

- Pulmonary rehabilitation: A program that includes exercise, education, and breathing techniques to help improve breathing, increase physical activity, and improve the overall quality of life for people with lung diseases such as COPD.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to treat respiratory problems. For example, lung cancer may require surgery to remove the tumour, and sleep apnea may require surgery to remove excess tissue in the throat that is blocking the airway.
- Lifestyle changes: Quitting smoking, avoiding environmental toxins, and maintaining a healthy diet and exercise can help prevent respiratory problems and improve overall health.
- Vaccination: Getting vaccinated against certain respiratory infections such as pneumonia and influenza can help prevent these infections and reduce the risk of complications.
It’s important to work with a healthcare provider to develop an individualized treatment plan that takes into account the specific condition, the patient’s overall health, and their preferences.
The Best Possible Preventive Measures to Safeguard Against Respiratory Issues
There are several preventive measures that can help safeguard against respiratory problems:
- Quit smoking: Smoking is the leading cause of preventable death worldwide and is a major risk factor for respiratory problems such as lung cancer, COPD, and asthma. Quitting smoking can greatly reduce the risk of these conditions.
- Avoid environmental toxins: Exposure to environmental toxins such as air pollution, pesticides, and hazardous chemicals can increase the risk of respiratory problems. Taking steps to reduce exposure to these toxins can help protect the lungs.
- Maintain a healthy diet: Eating a healthy diet that includes fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help support overall health and may reduce the risk of respiratory problems.
- Exercise regularly: Regular exercise can help improve lung function, increase muscle strength, and boost the immune system, which can help prevent respiratory problems.
- Get vaccinated: Vaccinations can help protect against respiratory infections such as influenza and pneumonia, which can lead to serious complications in people with underlying lung conditions.
- Keep a clean environment: Regular cleaning of the environment, especially in the living areas can help prevent respiratory infections.
- Avoid crowded places during flu season: Crowded places can be a breeding ground for respiratory infections, so it’s best to avoid them during flu season and other times when respiratory infections are more common.
- Seek medical attention when necessary: If you experience symptoms of a respiratory problem such as difficulty breathing, a persistent cough, or chest pain, it’s important to seek medical attention right away to prevent complications.
It’s worth noting that some of the preventive measures might be more effective than others depending on the situation, and a combination of different measures is recommended.
Some Simple Home Remedies at Home to Help Prevent the Problem
While some home remedies may provide some relief for mild respiratory problems, it is important to consult a Doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment. However, some simple home remedies that may help prevent or alleviate respiratory problems include:
- Steam inhalation: Inhaling steam can help loosen mucus and ease congestion in the respiratory tract. This can be done by adding a few drops of eucalyptus oil to a bowl of hot water and breathing in the steam through a towel.
- https://amzn.to/3VdtThH
- https://amzn.to/425v7h2


- Saltwater gargle: Gargling with salt water can help reduce inflammation and ease a sore throat and other symptoms caused by respiratory infections.
- Drinking fluids: Drinking plenty of fluids, especially water, can help keep the mucous membranes in the respiratory tract moist, which can help reduce the risk of infection.
- Rest: Getting enough rest and sleep is important for overall health and can help boost the immune system, which can help prevent respiratory problems.
- Humidity: Using a humidifier can add moisture to the air and help relieve dryness in the respiratory tract, which can be caused by dry indoor air.
- Yoga and breathing exercises: Yoga and breathing exercises can help improve lung function and increase muscle strength, which can help prevent respiratory problems.
- Herbal tea: Drinking herbal tea made with ingredients such as ginger, turmeric, and liquorice can help reduce inflammation in the respiratory tract and ease symptoms of respiratory problems.
It’s important to note that these remedies are not meant to replace medical treatment and should be used under the guidance of a professional Doctor. Also, not all remedies may be suitable for everyone, especially for people with chronic respiratory problems.
Causes of Allergy-Aggravating Respiratory Problems
Allergies can aggravate respiratory problems by causing inflammation and irritation in the airways. Some common allergens that can cause respiratory problems include:
- Dust mites: These tiny insects are commonly found in bedding, mattresses, and upholstered furniture. They can cause symptoms such as sneezing, runny nose, and asthma attacks.
- Pollen: Pollen from trees, grasses, and weeds can cause hay fever and allergic rhinitis, which can lead to congestion, sneezing, and asthma attacks.
- Mould: Mold spores can be found indoors and outdoors, and exposure to mould can cause symptoms such as sneezing, runny nose, and asthma attacks.
- Pet dander: Dander, or tiny flakes of skin, from animals such as cats and dogs can cause symptoms such as sneezing, runny nose, and asthma attacks.
- Cockroaches: Cockroaches can cause allergic reactions, especially in people with asthma, and can cause symptoms such as sneezing, runny nose, and asthma attacks.
- Chemicals: Exposure to chemicals such as cleaning products, pesticides, and perfumes can cause allergic reactions and aggravate respiratory problems.
- Food Allergies: Some people may have an allergic reaction to certain foods, which can cause respiratory symptoms such as difficulty breathing, wheezing and even anaphylaxis.
It’s important to note that not everyone will be allergic to the same things, and symptoms can vary from person to person. If you suspect you have an allergy, it is best to see an allergist or immunologist for proper diagnosis and treatment.
It is also important to mention that, in some cases, people with respiratory problems such as asthma can develop a condition called “allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillus” which is an allergic reaction to mould, specifically to Aspergillus fungus.
Cough is a natural phenomenon that can occur for a variety of reasons, and it can be classified into different types based on the underlying cause. The most common types of cough include:
- Acute Cough: this is a short-term cough that lasts less than three weeks, often caused by a cold, flu, or upper respiratory infection.
- Subacute cough: this is a cough that lasts between three and eight weeks, and is often caused by a viral infection, asthma, or postnasal drip.
- Chronic Cough: this is a cough that lasts longer than eight weeks, and can be caused by a variety of underlying conditions such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, or persistent infection.
- Productive Cough: this is a cough that produces mucus or phlegm. This type of cough is often caused by an infection or chronic respiratory condition.
- Nonproductive cough: this is a cough that does not produce mucus or phlegm. This type of cough can be caused by conditions such as asthma, postnasal drip, or acid reflux.
- Wet Cough: This type of cough produces a lot of mucus, also called phlegm.
- Dry cough: This type of cough is characterized by a hacking or rasping sound, with no mucus production.
It’s important to note that some coughs can be caused by more than one underlying condition. It’s best to consult with a Doctor to determine the underlying cause of a cough and receive appropriate treatment.
In summary, Cough can be classified into different types based on the
Simple Preventive Measures to Protect Oneself from Cough During Winter
There are several preventive measures that can help protect oneself from cough during the winter:
- Wash Your Hands Regularly: This can help to reduce the spread of germs that can cause colds and flu.
- Get a flu shot: This can help to protect against the flu, which is a common cause of cough during the winter.
- Stay Warm: Cold weather can make the airways more sensitive, which can lead to coughing. Staying warm can help to reduce the risk of a cough.
- Keep the Air Moist: Dry air can irritate the airways and make coughing worse. Using a humidifier or keeping a bowl of water near a heat source can help to keep the air moist.
- Avoid Smoking and Secondhand Smoke: Smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke can irritate the airways and make coughing worse.
- Avoid Exposure to Irritants: Common irritants such as pollution, chemicals, and dust can make coughing worse.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking enough water can help to keep the mucous membranes in the respiratory system moist, which can help to reduce coughing.
- Eat Healthily: Eating a balanced diet that includes fruits and vegetables can help to boost the immune system, which can help to protect against colds and flu.
- Exercise Regularly: Regular physical activity can help to strengthen the immune system and reduce the risk of colds and flu.
It’s worth noting that these preventive measures can be helpful, but they may not completely prevent cough during the winter. If you do develop a cough, it’s best to consult with a qualified healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause and receive appropriate treatment.
Consuming Honey in Winter is Beneficial for the Health

Using honey in winter can be beneficial for health as it has antimicrobial and antioxidant properties. Honey can help to soothe a sore throat and reduce coughing by coating the throat and reducing irritation. It also has antibacterial properties, which can help to fight off infections that can cause a cough.
Honey is also a natural source of antioxidants, which can help to boost the immune system and protect against colds and flu.
Honey has also been traditionally used as an expectorant, which can help to loosen and remove mucus from the respiratory tract, making it easier to cough up and reducing the duration of a productive cough.
Honey can be consumed directly or can be added to tea, warm water or other warm drinks. It is important to note that honey should not be given to children under one year of age as it can cause botulism.
In summary, using honey in winter can be beneficial for health as it has antimicrobial and antioxidant properties, can help to soothe a sore throat, reduce coughing, fight off infections and boost the immune system. It’s always best to consult with a qualified healthcare professional before using honey as medicine.
DISCLAIMER: The contents of this article are intended to raise awareness about common health issues and should not be viewed as sound medical advice for your specific condition. You should always consult with a licensed medical practitioner prior to following any suggestions outlined in this article or adopting any treatment protocol based on the contents of this article.