Pumpkin Seeds: Nutrition, Health Benefits, Uses, and Safety Guide
Introduction
Small in size but powerful in nutrition, pumpkin seeds have quietly earned their place among the most valuable natural foods. Often discarded while preparing pumpkins, these flat green seeds are packed with nutrients that support immunity, heart health, sleep quality, and overall wellness.

Across cultures, pumpkin seeds have been roasted, eaten raw, ground into powders, or used in traditional remedies. Today, modern nutrition science confirms what traditional wisdom already knew. These seeds are not just a snack. They are a functional food that fits easily into everyday meals.
This article explores pumpkin seeds in depth, explaining what they contain, how they benefit the body, how to use them correctly, and who should be cautious.
What are the health benefits of pumpkin seeds?
Pumpkin seeds are a suitable sourceTrusted Source of healthy fats, magnesium, and other nutrients that enhance heart and bone health.
They are also rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids and antioxidants such as selenium and beta carotene. Additionally, they are a high source of iron. One cup of pumpkin seeds contains 9.52 milligrams (mg) of iron, a significant portion of the 18 mg recommended daily allowance (RDA)Trusted Source for premenopausal females and 8 mg for males and postmenopausal females.
What Are Pumpkin Seed?
Pumpkin seeds come from pumpkins and are also known as pepitas. They are oval, flat, and usually light green when the outer white shell is removed. Pumpkin seeds are edible both with and without their shells, depending on the variety.
They are widely consumed across Asia, Europe, and the Americas. Pumpkin seeds are valued not only for their taste but also for their impressive nutritional profile, which includes healthy fats, plant protein, vitamins, and minerals.
Nutritional Profile
These seeds are nutrient-dense, meaning they provide a high amount of nutrients relative to their calories.
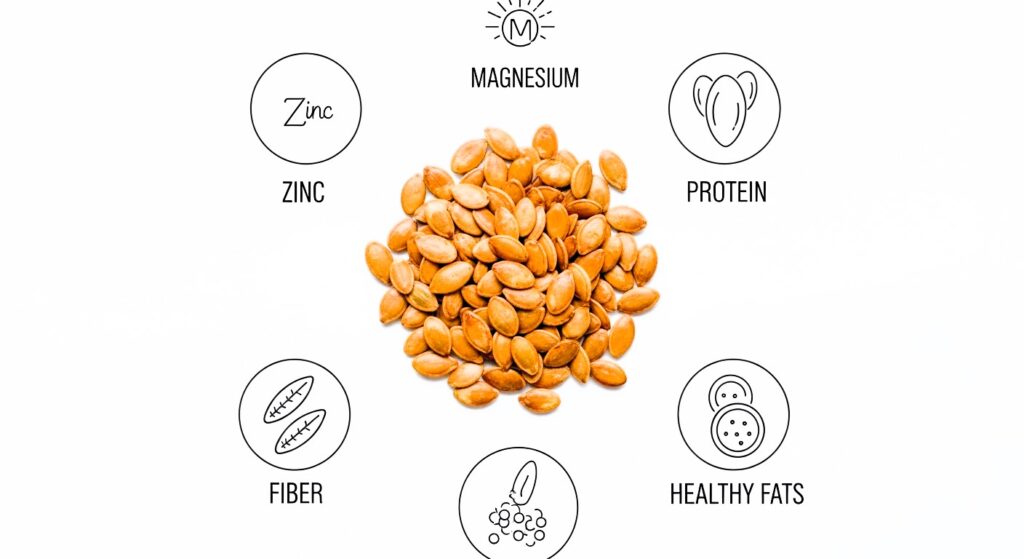
Key Nutrients
- Zinc
- Magnesium
- Iron
- Protein
- Healthy fats
- Antioxidants
- Fiber
Just one small handful can contribute significantly to daily mineral needs, especially zinc and magnesium, which many people lack.
Health Benefits
Supports the Immune System
Seeds are one of the best plant sources of zinc. Zinc plays a critical role in immune cell development and function. Adequate zinc intake helps the body fight infections and supports faster recovery from illness.
This makes seeds especially valuable during seasonal illnesses and periods of physical stress.
Promotes Heart Health
These seeds contain healthy fats, antioxidants, and magnesium. These nutrients help regulate blood pressure, reduce inflammation, and support healthy cholesterol levels.
Magnesium, in particular, is linked with reduced risk of heart disease. Regular consumption of seeds can support cardiovascular health as part of a balanced diet.
Supports Better Sleep
These seeds are a natural source of tryptophan, an amino acid involved in the production of serotonin and melatonin. These compounds regulate mood and sleep cycles.
Magnesium in seeds also plays a role in relaxing muscles and calming the nervous system, which can improve sleep quality when consumed regularly.
May Support Prostate and Men’s Health
Seeds have traditionally been used to support prostate health. Some studies suggest that compounds in seeds may help maintain normal prostate function and urinary health, especially in older men.
This benefit is often linked to zinc and specific plant compounds found in the seeds.
Helps with Blood Sugar Control
These seeds have a low glycemic impact and contain fibre, protein, and magnesium. These nutrients help stabilise blood sugar levels by slowing digestion and improving insulin sensitivity.
Including seeds in meals may be helpful for people managing blood sugar, although they should not replace medical treatment.
Supports Digestive Health
Seeds provide dietary fibre, which supports digestion and regular bowel movements. Fibre also nourishes beneficial gut bacteria, which play a role in immune health and nutrient absorption.
Skin and Hair Benefits
The zinc, antioxidants, and healthy fats in seeds support skin repair and hydration. These nutrients also contribute to hair strength and scalp health when consumed regularly as part of a nutrient-rich diet.
How to Eat 
How to Eat
Raw Pumpkin Seeds
Raw seeds retain their natural nutrients. They can be eaten on their own or added to smoothies, yoghurt, or salads.

Roasted Seeds
Roasting enhances flavour and crunch. Dry roast or lightly roast with minimal oil to preserve nutrients.
Seed Powder
Ground pumpkin seeds can be added to soups, sauces, or smoothies. This is helpful for people who prefer softer textures.
Pumpkin Oil
Pumpkin seed oil is used in small amounts as a finishing oil for salads. It should not be used for high-heat cooking.
How Much Pumpkin Seeds Should You Eat
A common recommended portion is one to two tablespoons per day. This amount provides nutritional benefits without excessive calorie intake.
Moderation is important, as pumpkin seeds are calorie-dense.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions
Seeds are generally safe for most people. However, some points to consider:
- Overconsumption may cause digestive discomfort
- Salted varieties may increase sodium intake
- People with seed allergies should be cautious
- Those on mineral supplements should avoid excessive intake
Pregnant and breastfeeding individuals can consume pumpkin seeds in normal food amounts unless advised otherwise by a healthcare provider.

Pumpkin Seeds vs Other Seeds
Compared to other seeds:
- Higher zinc than flax and chia seeds
- More magnesium than sunflower seeds
- Higher protein than sesame seeds
Each seed has unique benefits, but pumpkin seeds stand out for immune and mineral support.
FAQs About Pumpkin Seeds
1. Are pumpkin seeds good for immunity
Yes. Pumpkin seeds are rich in zinc and antioxidants that support immune function.
2. Can pumpkin seeds help with sleep
They contain magnesium and tryptophan, which support relaxation and sleep quality.
3. Are pumpkin seeds good for weight management
They are filling due to protein and fiber but should be eaten in moderation due to calories.
4. Can children eat pumpkin seeds
Yes. They are nutritious but should be given in age-appropriate forms to avoid choking.
5. Is pumpkin seed oil better than whole seeds
Oil is concentrated, while whole seeds provide fibre and protein. Both have benefits.
6. Can pumpkin seeds be eaten daily
Yes. Daily consumption in moderate amounts is generally safe and beneficial.
This post contains affiliate links, which means I earn a commission if you purchase through these links. This comes at no additional cost to you and helps support the content I create. I only promote products/services I believe in and use myself. Your support is greatly appreciated!
Disclaimer: The content in this article is intended for informational and educational purposes only. It provides insights, tips, and general guidance on health, beauty, and wellness, but it is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
Always consult a qualified healthcare professional for personal medical concerns. For more information about our approach to health and wellness content, please read our Health & Wellness Disclaimer.
References
- Healthline: Pumpkin Seeds Nutrition and Benefits
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/11-benefits-of-pumpkin-seeds - WebMD: Pumpkin Seeds Health Benefits
https://www.webmd.com/diet/health-benefits-pumpkin-seeds - Harvard Health: Magnesium and Heart Health
https://www.health.harvard.edu - National Institutes of Health: Zinc Fact Sheet
https://ods.od.nih.gov
Internal Links
- Black Seeds: Health Benefits and Uses
- Flax Seeds: Nutrition and Health Benefits
- Chia Seeds: https://mrpo.pk/chia-seeds/
- Immune-Boosting Foods



